In this video, first, we will demonstrate how to simulate and synthesize a circuit, displaying prime numbers. In our circuit, “PIC16F84_Prime_number_generator_Sim_DE10-Lite” we will use a PIC MCU VHDL code.
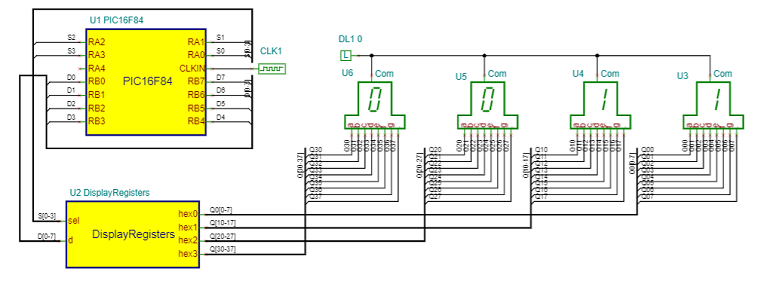
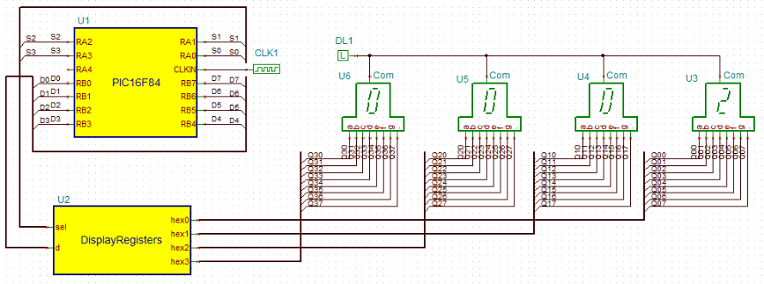
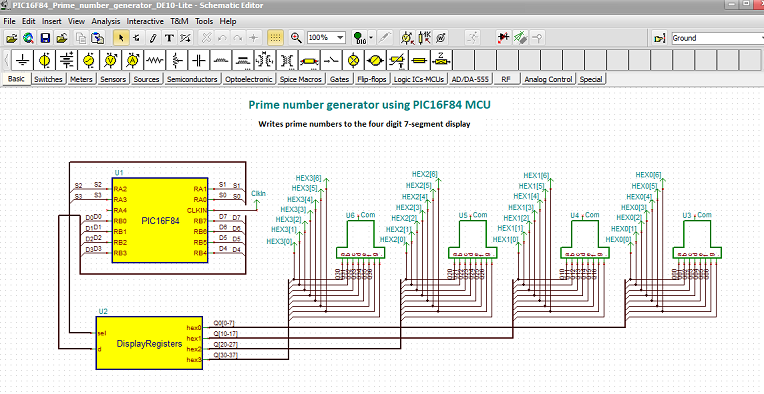
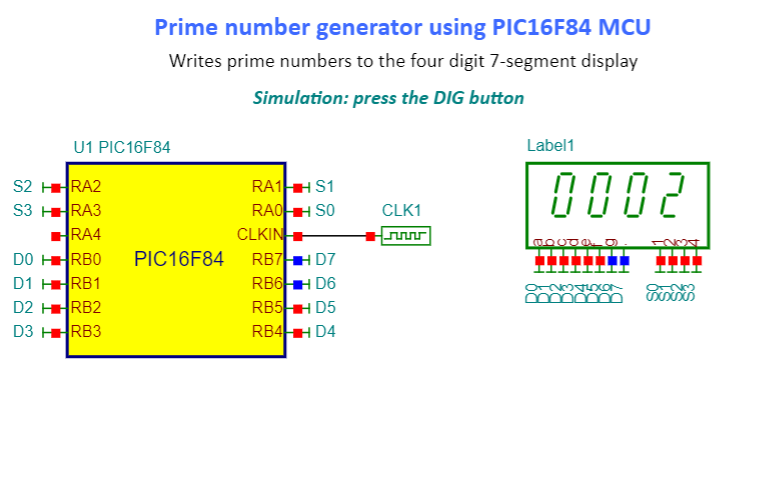
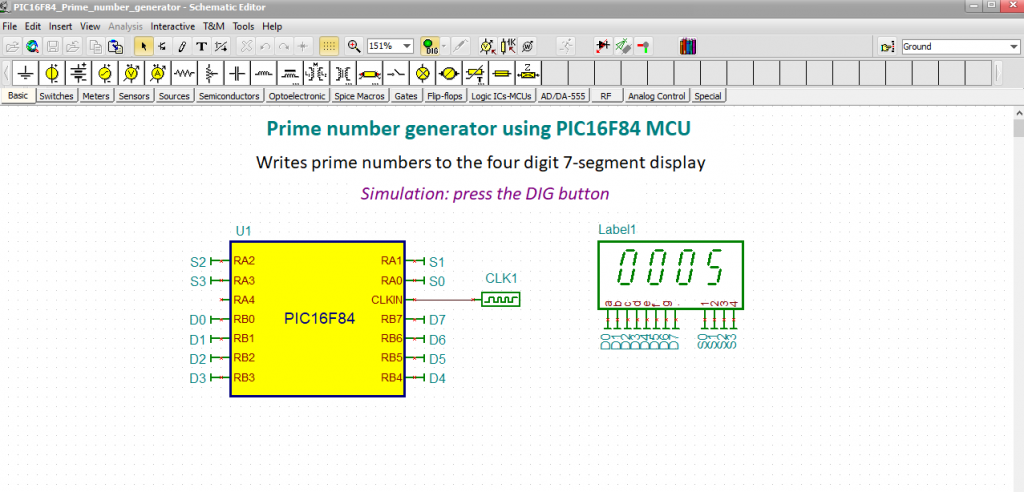
PIC16F84_Prime_number_generator_Sim_DE10-Lite circuit
This circuit calculates prime numbers between 1 and 9999 and shows them on a 4-digit 7-segment display.
The four digits have 32 pins (4 times 8).
Given that the PIC has limited number of lines to control the display, we use an array of registers, which is implemented in the DisplayRegisters VHDL macro.
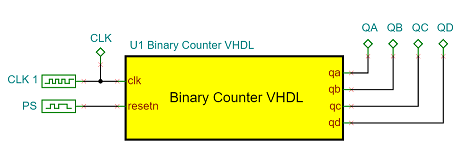
The Display Registers
The register array is implemented in the DisplayRegisters VHDL macro.
The registers will be written by the PIC chip.
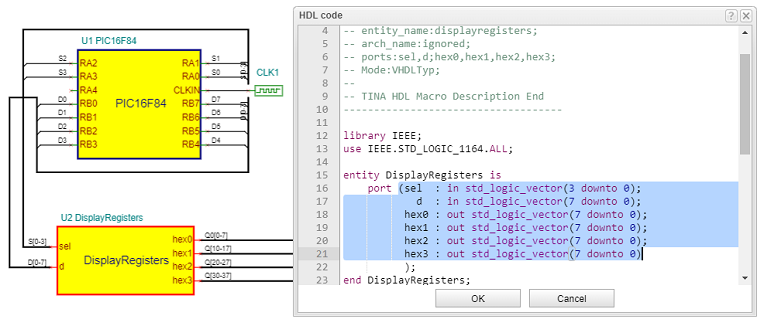
The macro has two inputs: „sel” and „d ”. Both are VHDL standard logic vector connected to the MCU port by buses.
Each registered output goes to the appropriate digit passing the 7-segment codes to the display.
When one line of the sel input goes low, then the 7-segment code, – asserted on the ‘d’ bus by the MCU, – will be stored in the appropriate output register.
Note, that to turn a segment on, the proper pin should be at a high level, because our display is common cathode type.
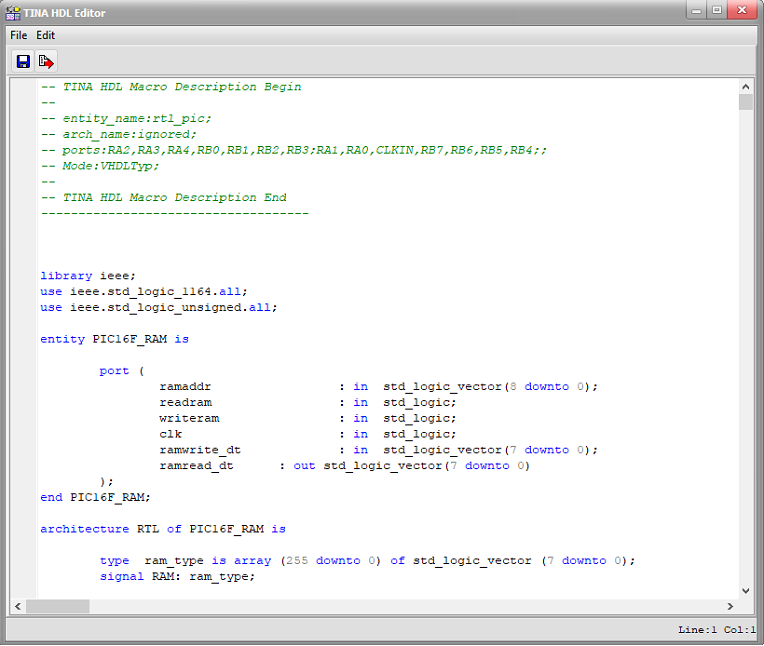
The PIC16F84 MCU model
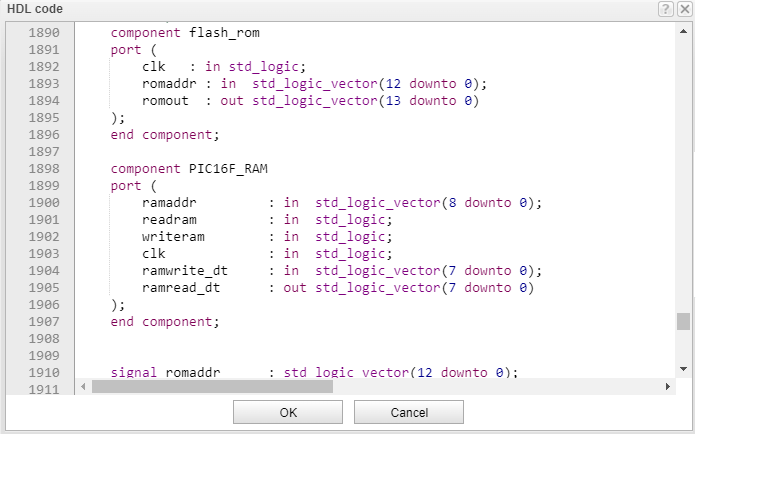
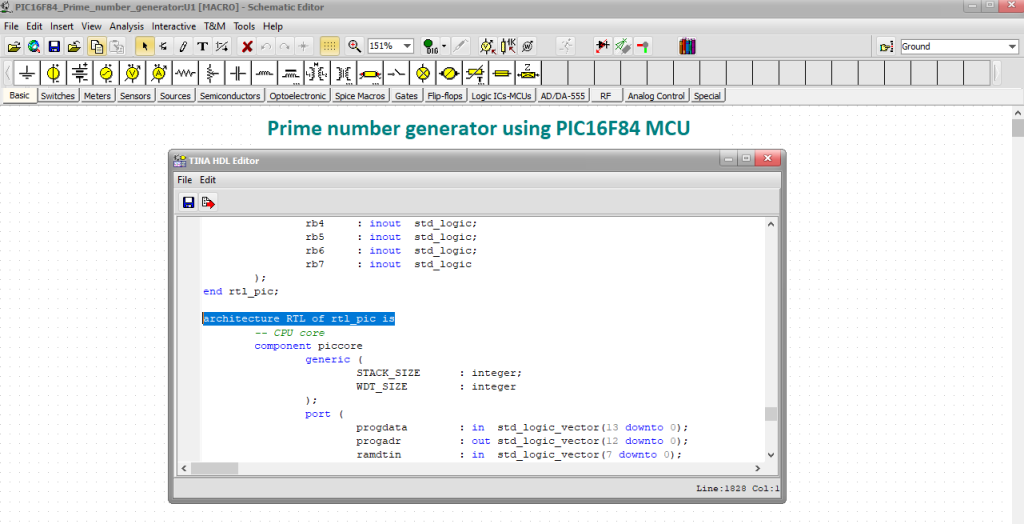
In this circuit, the PIC MCU model is written in VHDL.
Next, we will look at the VHDL code which is implemented in the PIC16F84 MCU model. Among others we will check the the top-level entity, then the rtl_pic entity, in which we instantiate and connect the main components.
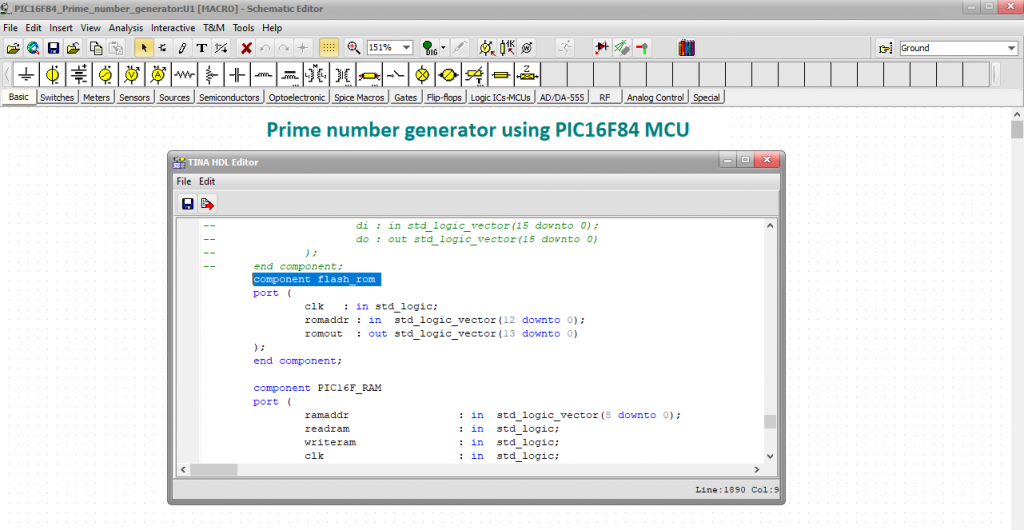
We will also take a look at the flash_rom entity, where the prime number generator program was loaded.
Next, in line 76 you we check the case construction which describes the ROM functionality.
Finally, we look at the ROM content of the program code written in C, which we have already converted to this VHDL code.
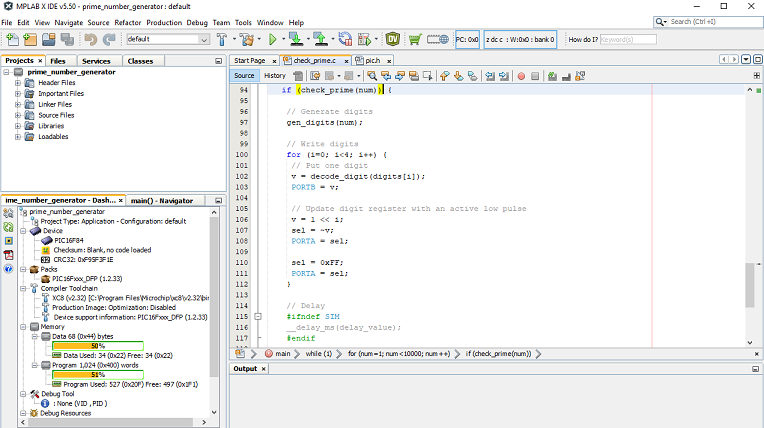
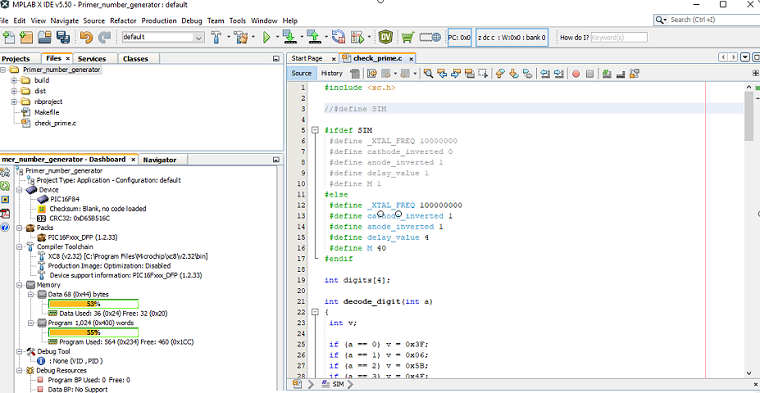
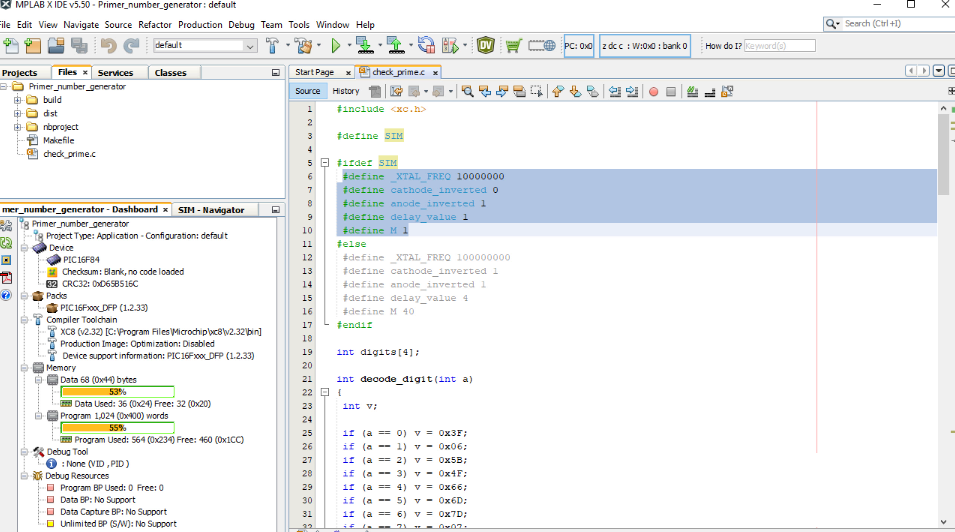
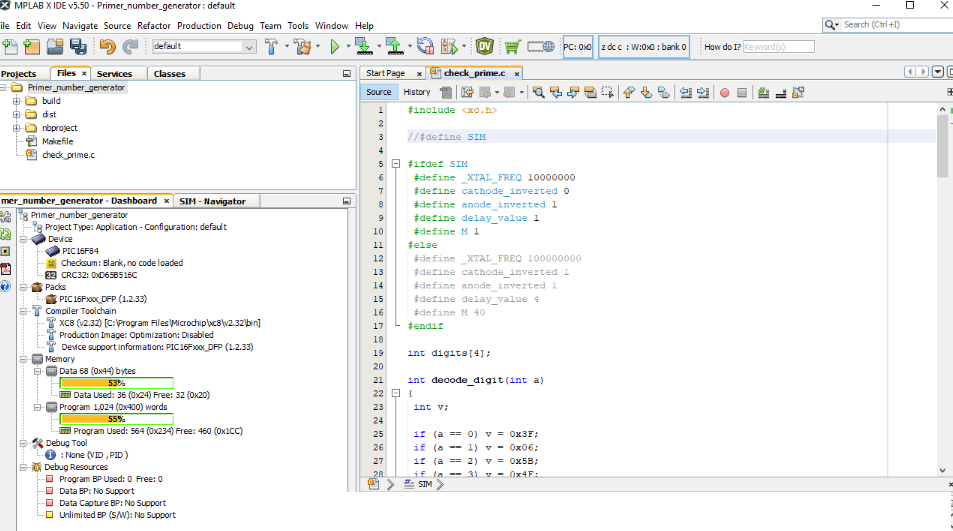
The C code
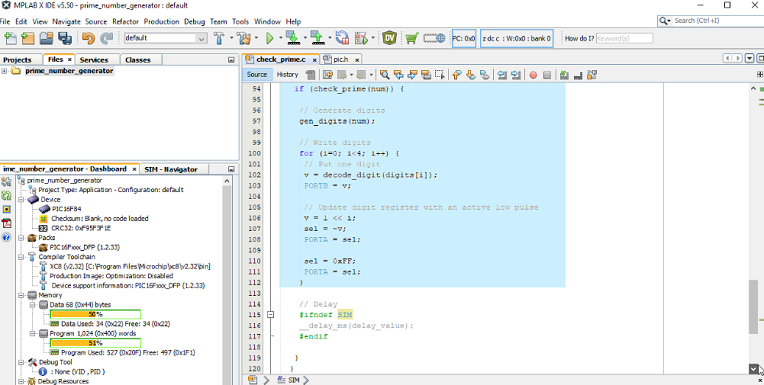
In the following we will look at the C code.
It is good to know that the project was created, and the program was developed with the free version of Microchip MPLAB IDE and their Microchip XC8 compiler.
Running the simulation using TINACloud’s Schematic Editor
After that we run the simulation in TINACloud Schematic Editor.
It is also possible to follow the transitions of the digital nodes, if you switch to the “Show Digital Node States” option.
Making the main difference in the C code for the synthesis
Next, we return to the MBLAB editor to make the main difference in the C code for the synthesis.
We comment the SIM definition out. Thus, we have defined new constants, like the processor speed in(50 MHz).
This is the oscillator frequency of the DE10-Lite FPGA board.
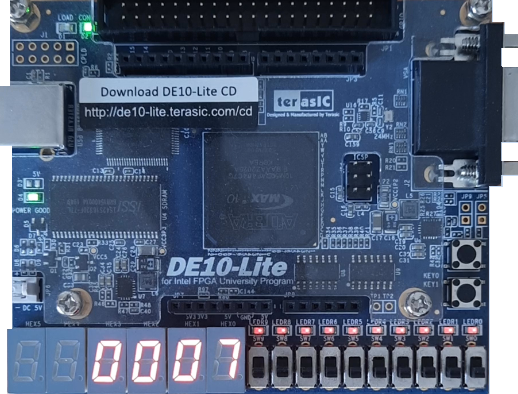
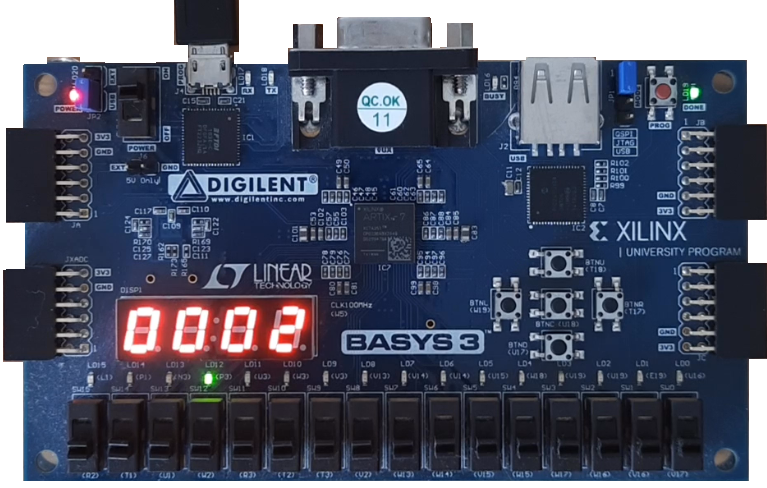
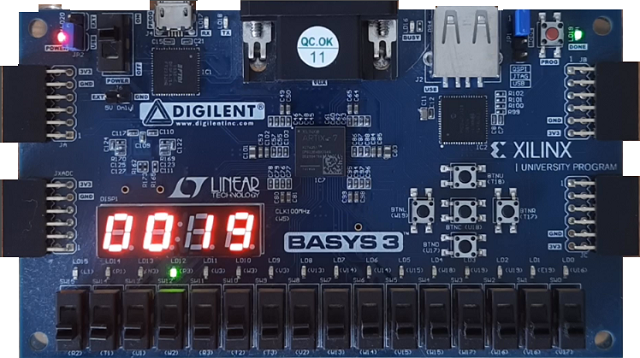
Testing our circuit with the Terasic DE10-Lite FPGA board
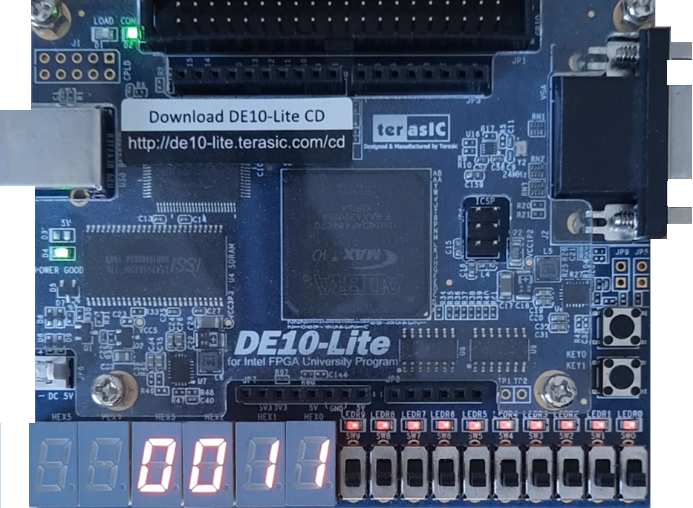
Finally, we will test our circuit, ” PIC16F84 Prime number generator DE10 Lite ” in a real environment using the Terasic DE10-Lite FPGA board.
We will export the VHDL to the Quartus Prime Lite software, compile it and load the resulting bitstream into the Terasic DE10-Lite FPGA development board.
As soon as we finish programming the hardware and we turn the Terasic DE10-Lite board on, we can see the prime numbers written on the display as expected.
Click here to watch our video.
You can learn more about TINA here: www.tina.com
You can learn more about TINACloud here: www.tinacloud.com