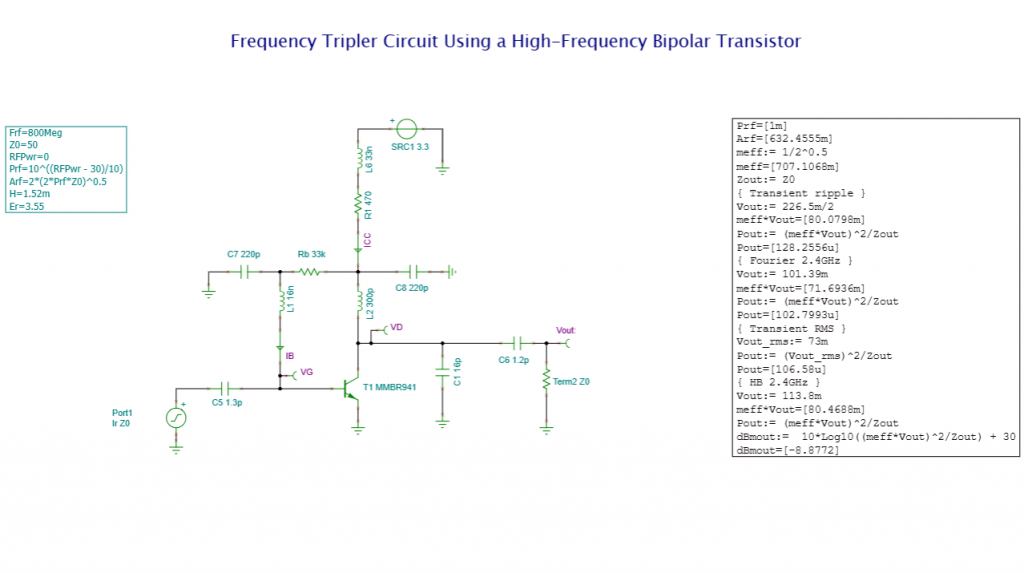
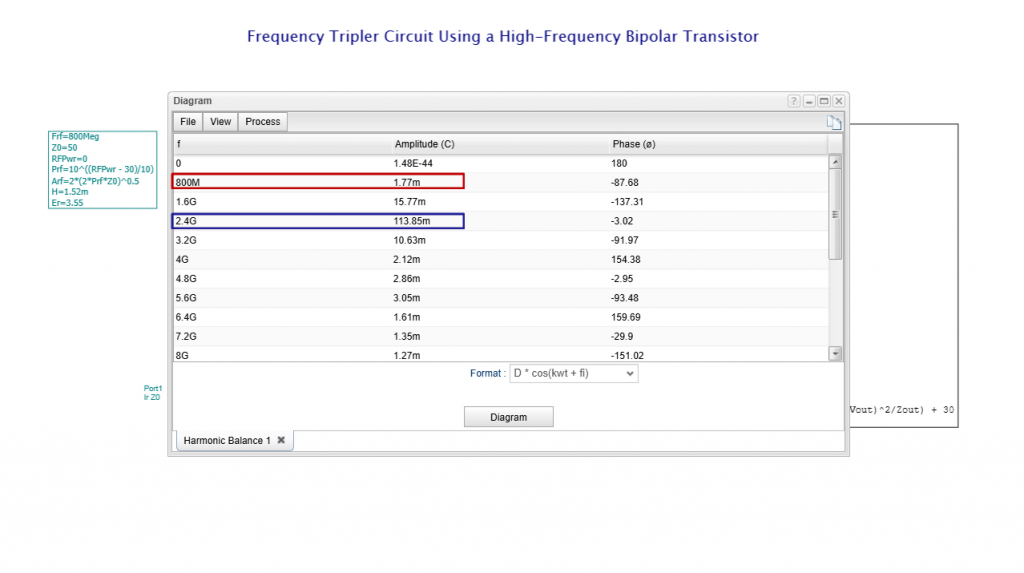
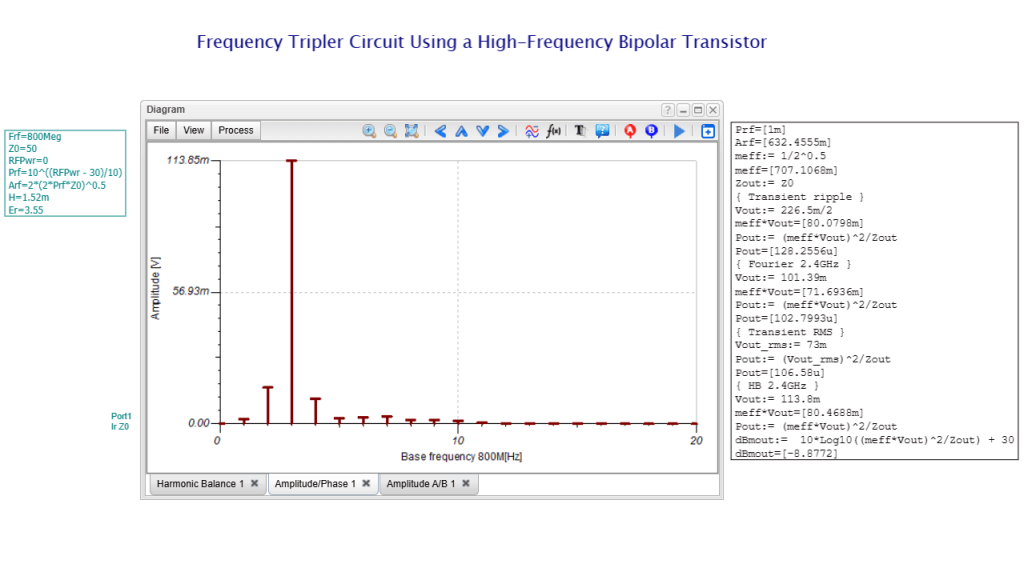
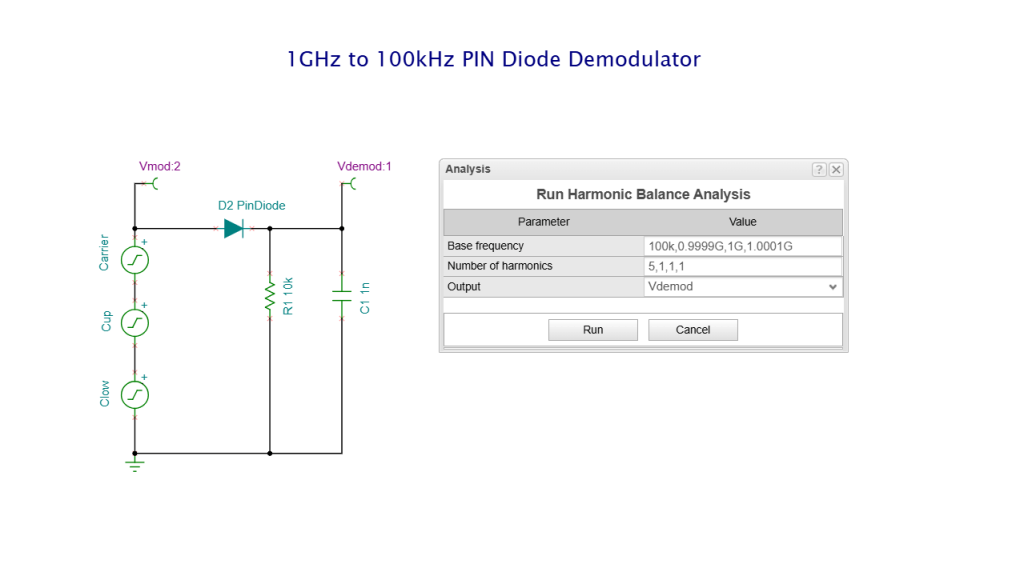
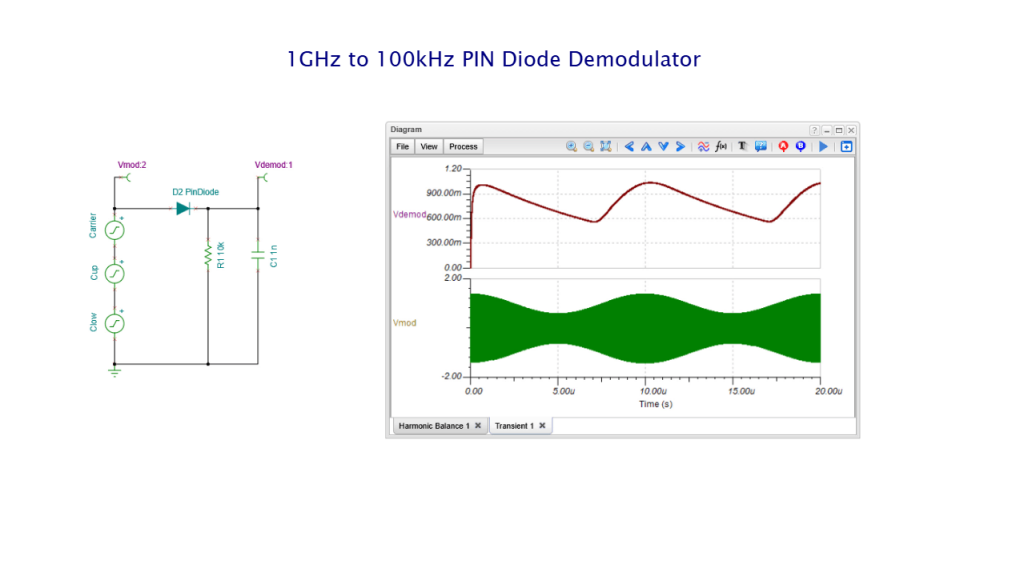
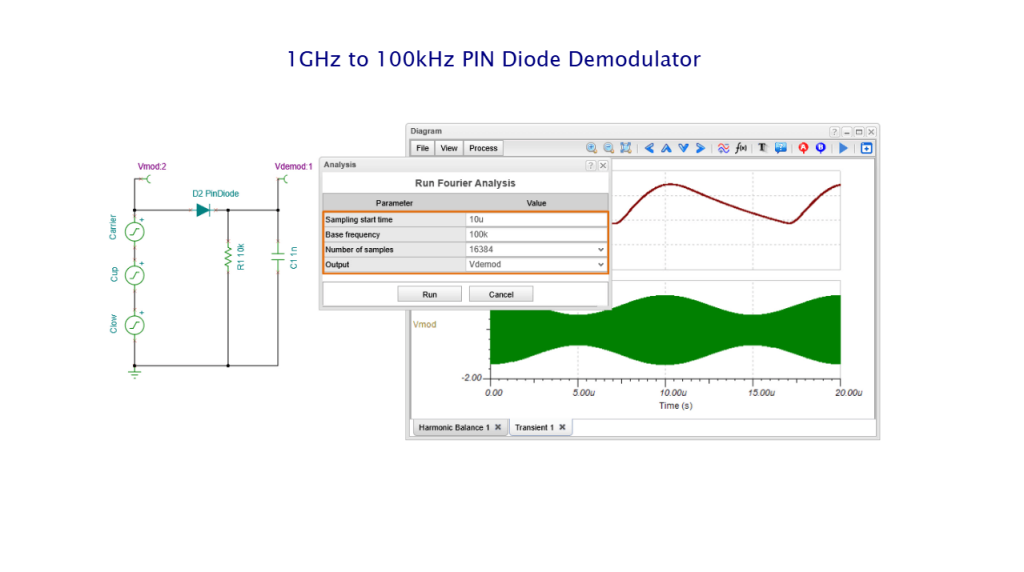
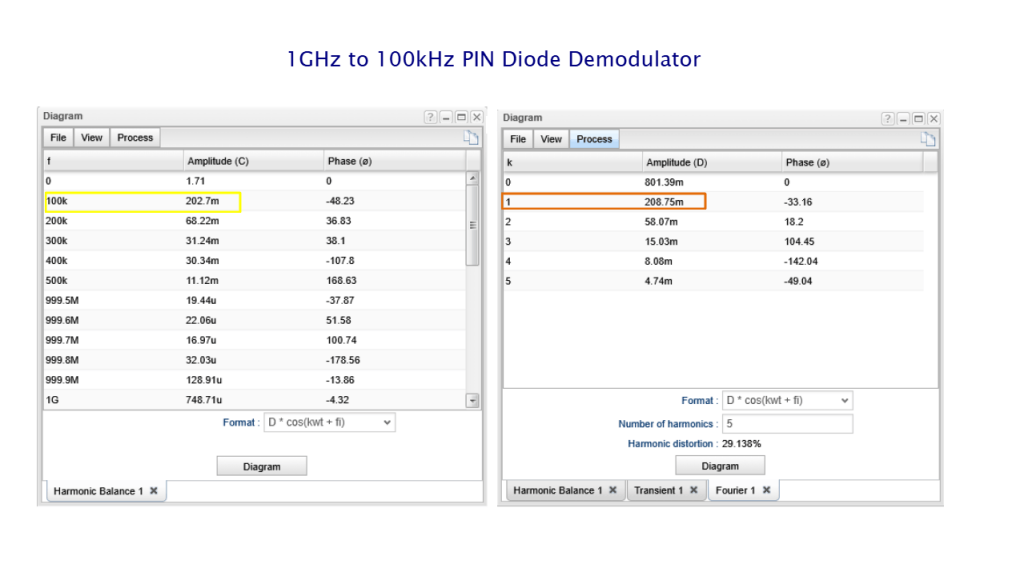
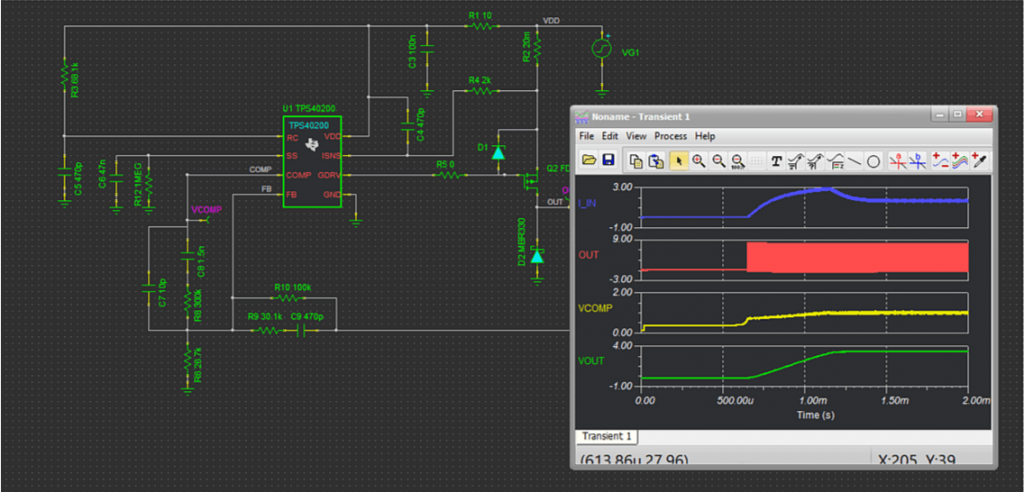
We have refreshed our “What is TINA and TINACloud?” informational video. This post introduces the updated content and outlines the key points covered.
Welcome to TINA & TINACloud: the powerful yet affordable circuit simulation and PCB design software packages available offline and online—now with built-in AI support. TINA and TINACloud are used by more than 100,000 users in 200 countries and 26 languages.
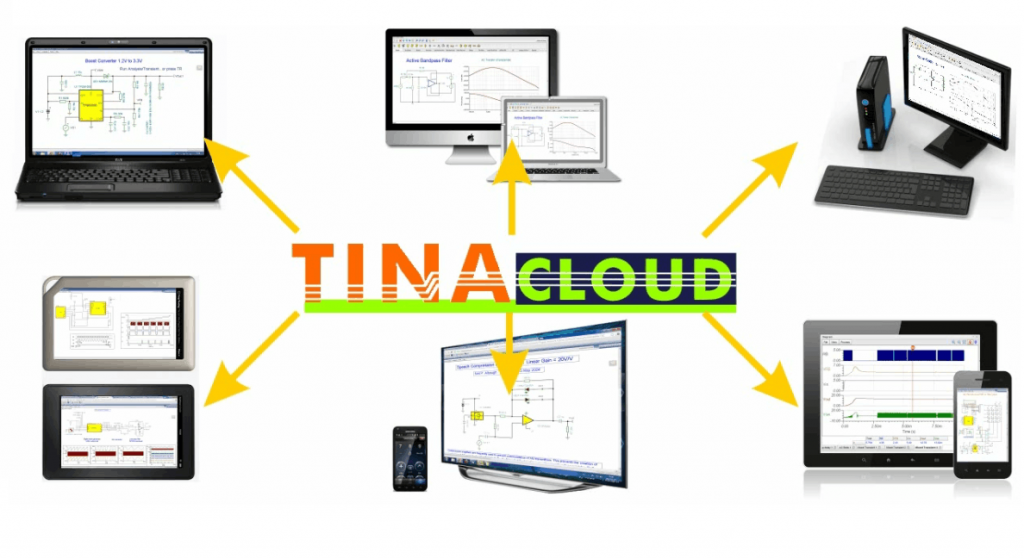
Multi-Platform Accessibility
TINA can be downloaded and installed on your computer. From TINA v16, it is available for Windows, Apple macOS, and major Linux distributions, including Ubuntu, Mint, SUSE, and even Raspberry Pi OS. Now, TINA is also available in light and dark mode, allowing you to enjoy a consistent, powerful experience whether you’re in the lab, at your desk, or on the go.
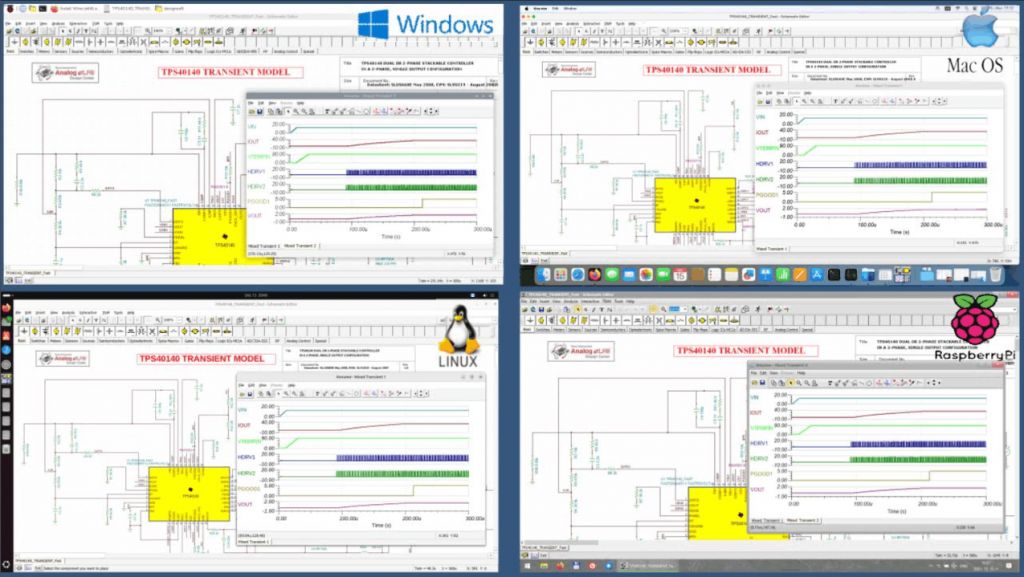
The online TINACloud runs in your browser without any installation, anywhere in the world where internet is available.
Built-in AI Support & Hardware Acceleration
AI tools in TINA and TINACloud offer a flexible, user-friendly interface for various engineering tasks, including:
- Providing information on circuits and designing LDO and SMPS power supply circuits.
- Designing active/passive filters, analog oscillators, and digital clock generators.
- Selecting and redesigning evaluation circuits from different manufacturers.
- Generating Arduino code for rapid prototyping and complex Python code for custom analysis.
- Image recognition with Python or MCU.
- Creating step-by-step solutions for DC/AC circuits, quizzes, and riddles.
The AI support in the offline TINA provides flexibility and privacy, now featuring expanded AI hardware acceleration supporting NVIDIA, AMD, and Intel Arc GPUs. You can use local AI models without internet connectivity or leverage cloud-based AI services.
AI Application Examples:
- Redesigning a Switch Mode Power Supply (SMPS): TINA includes SMPS models from leading manufacturers like TI, Infineon, Analog Devices, and more. You can redesign these using natural language. For example, by telling the AI to “set the output voltage to 3V” or “change the output voltage to 8V,” the circuit is automatically updated.
- Colpitts Oscillator: Simply enter “Set the frequency to 1MHz,” and the redesigned circuit oscillates at the requested frequency.
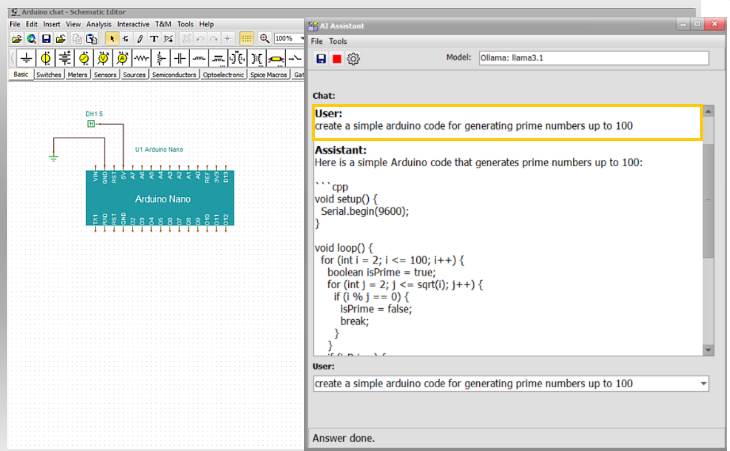
- Arduino Code Generation: Request the AI to “Create a simple Arduino code for generating prime numbers up to 100,” then compile and verify the results using TINA’s Serial Monitor.
- Education & Analysis: Generate custom Python code to compare with simulation results or create step-by-step DC/AC solutions in TINACloud.
- Quizzes and Riddles: AI can analyze circuits to create interactive quizzes or riddles, providing detailed evaluations of learning progress.
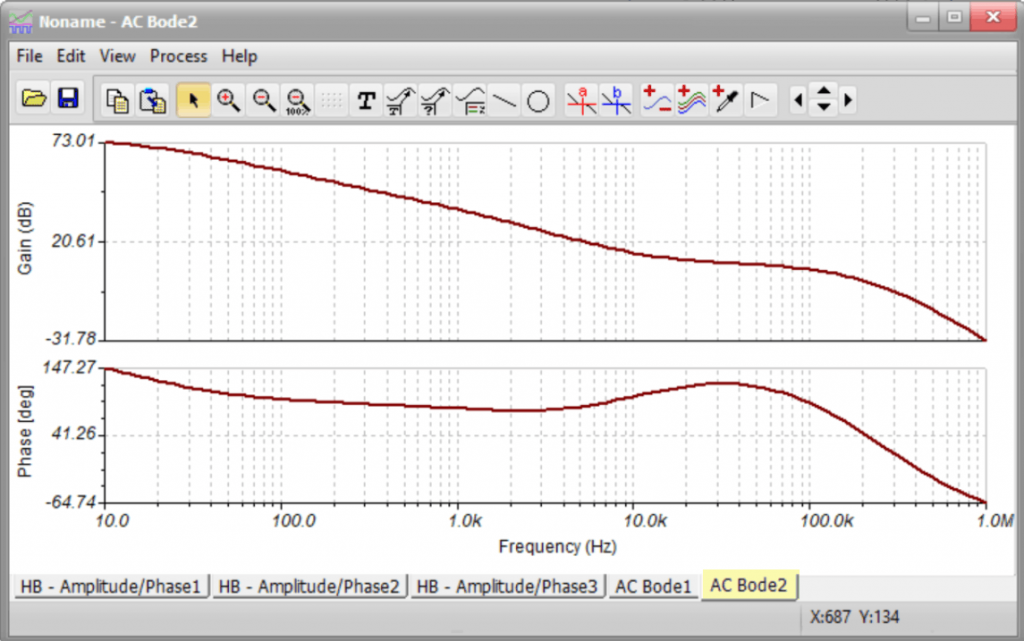
Advanced Circuit Analysis & Design
TINA and TINACloud allow you to analyze and design:
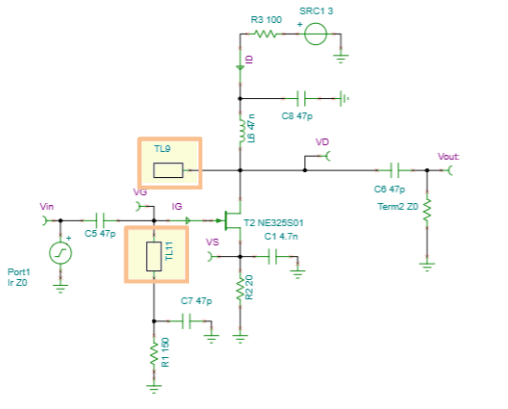
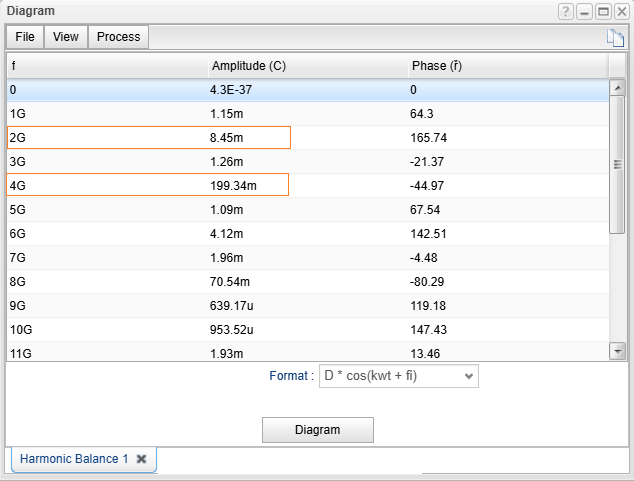
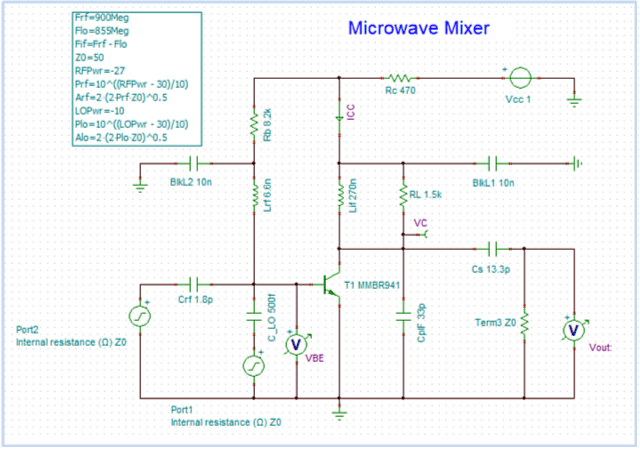
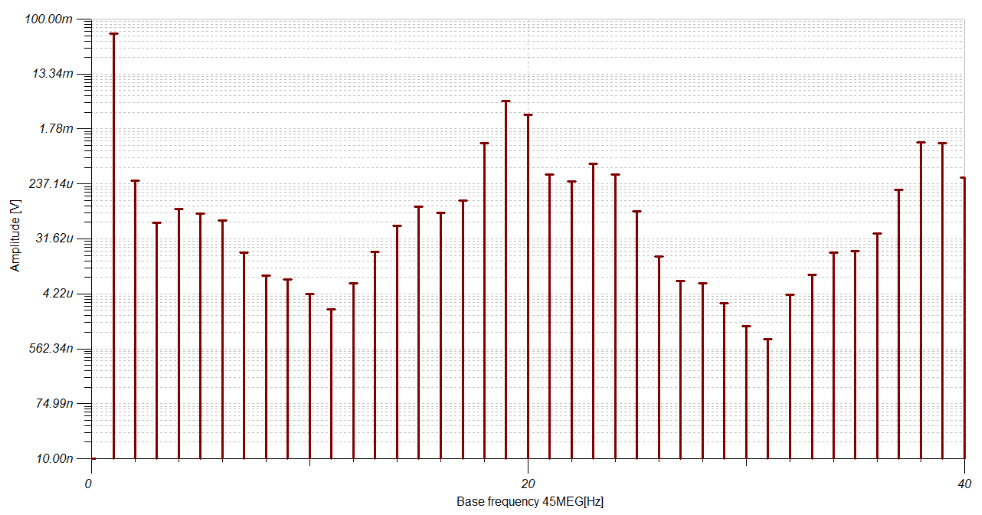
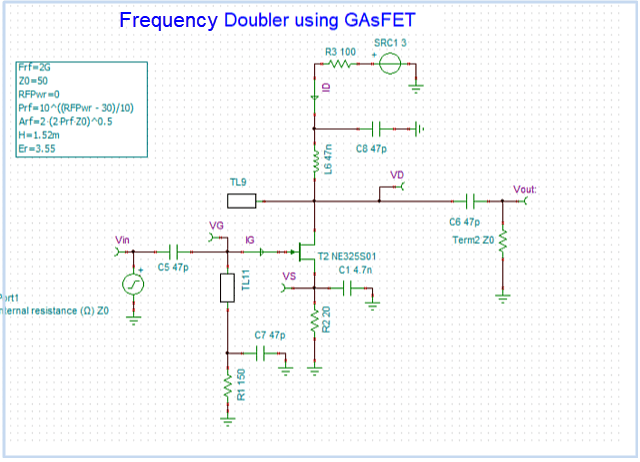
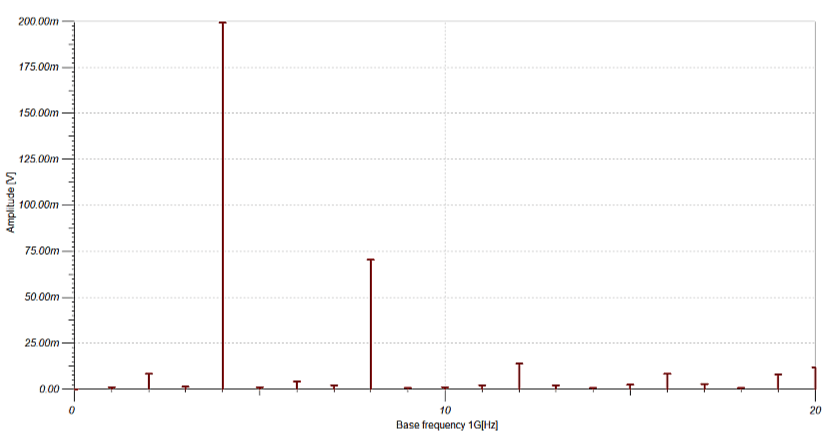
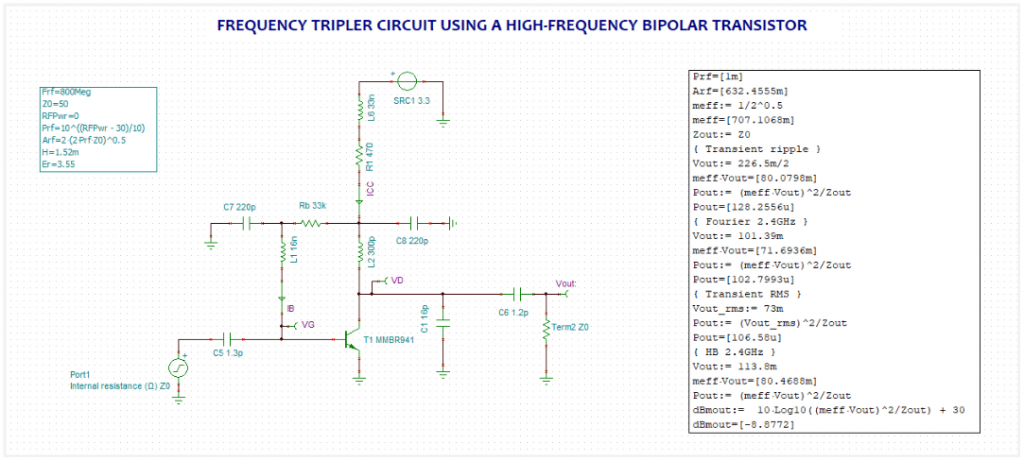
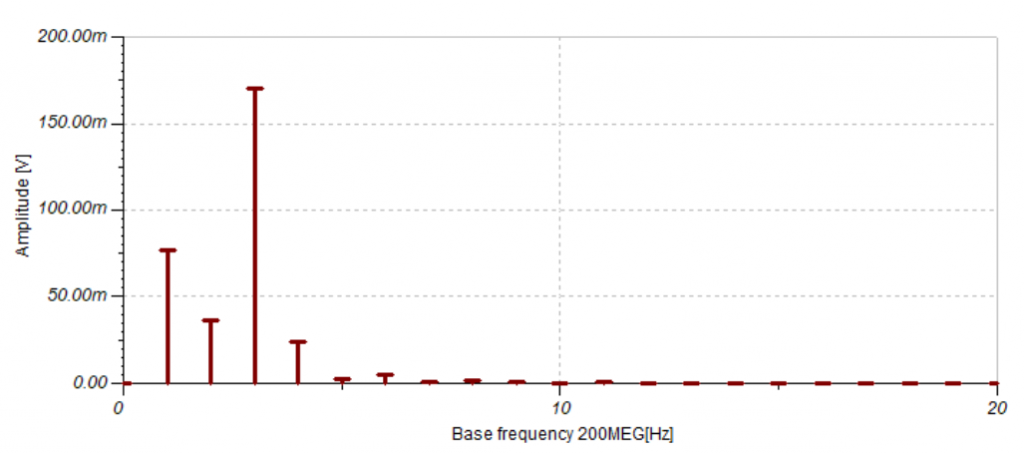
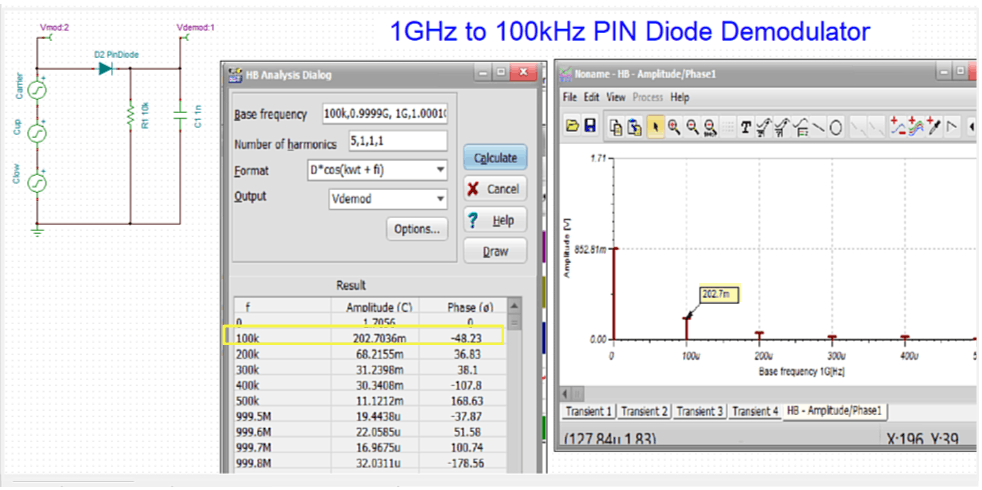
- Analog, Digital, Mixed, and RF circuits.
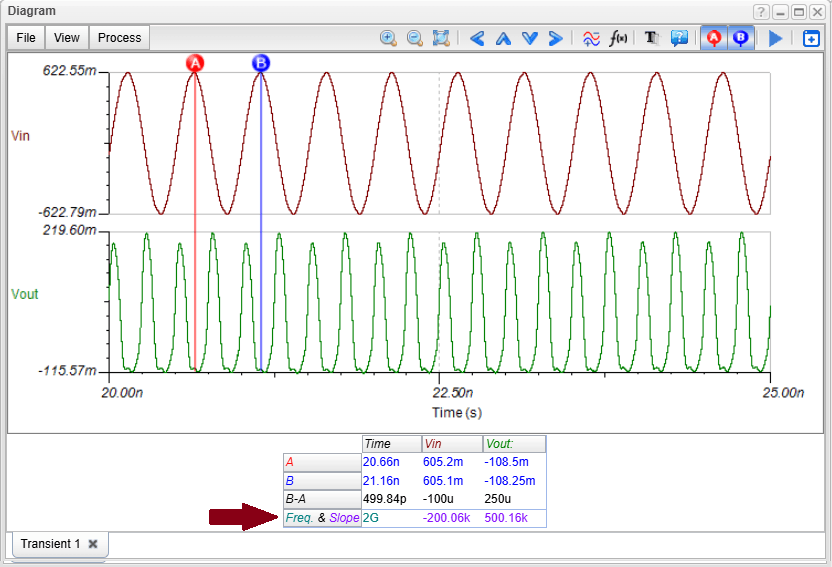
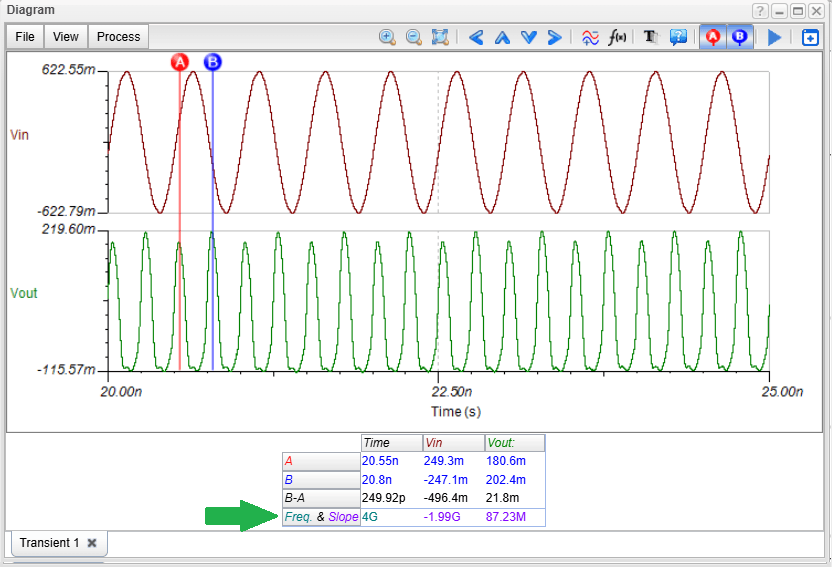
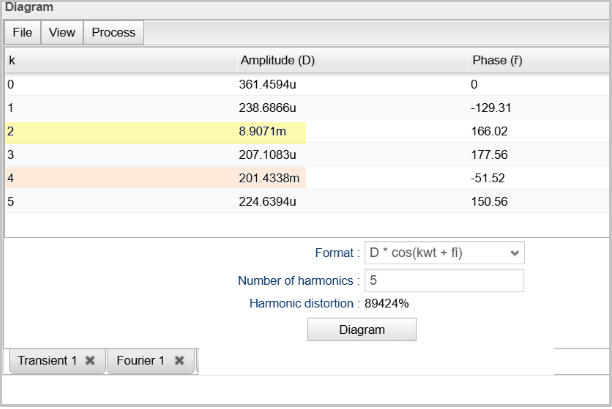
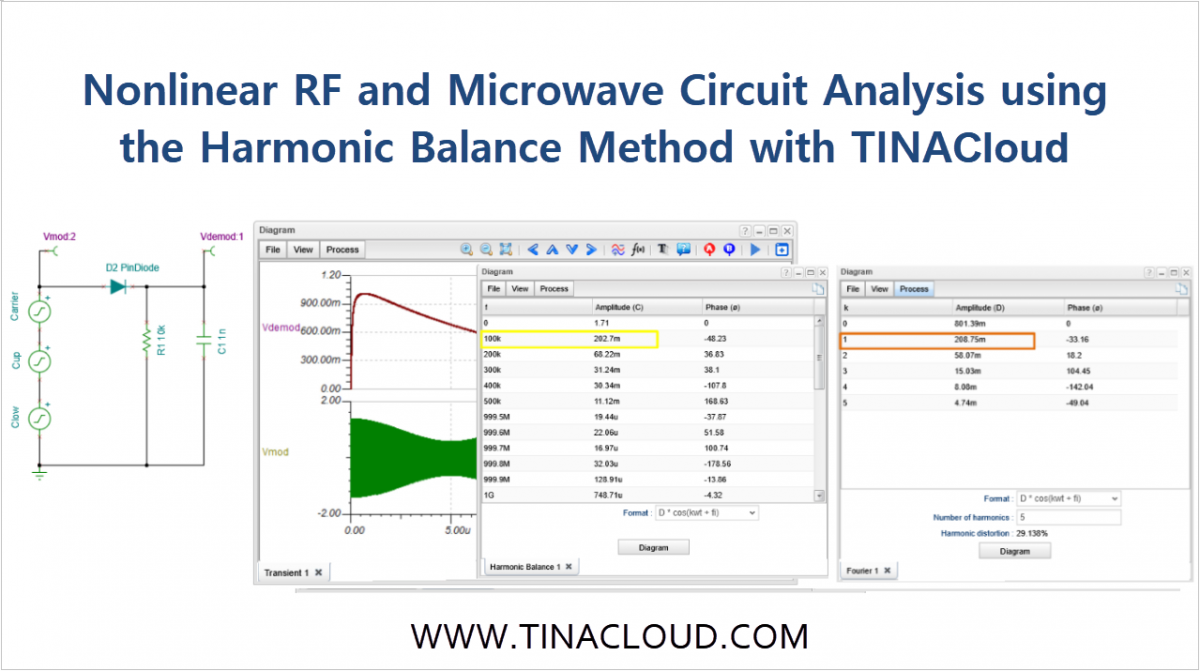
- Nonlinear RF and microwave circuits using Harmonic Balance.
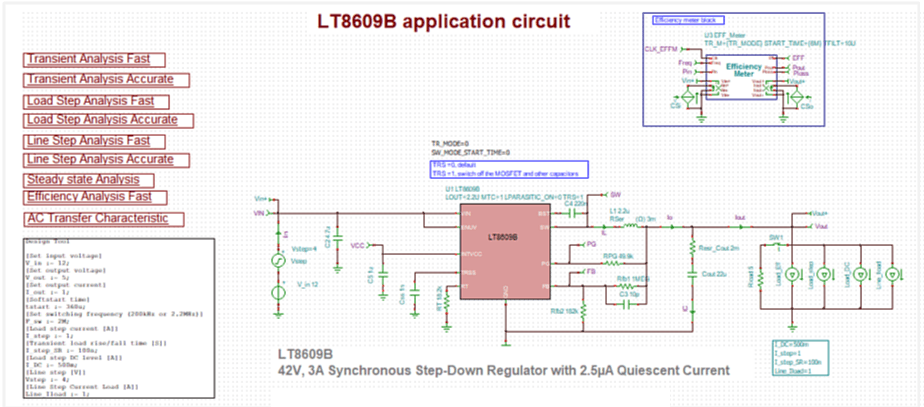
- Switched Mode Power Supplies, Communication, and Optoelectronic circuits.
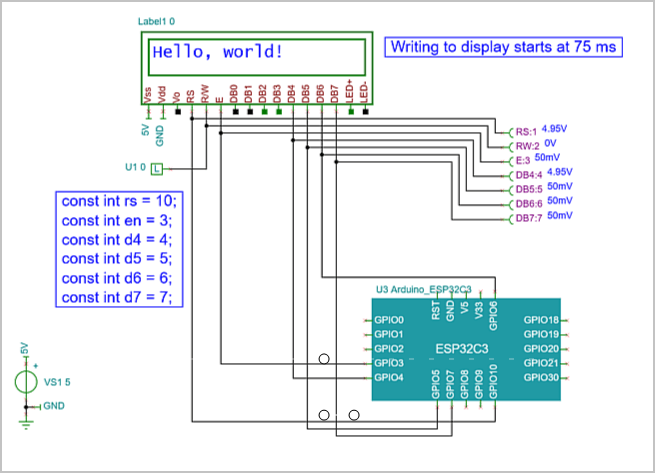
- Microcontroller applications in digital or mixed circuit environments (including the newly supported ESP32 microcontroller series).
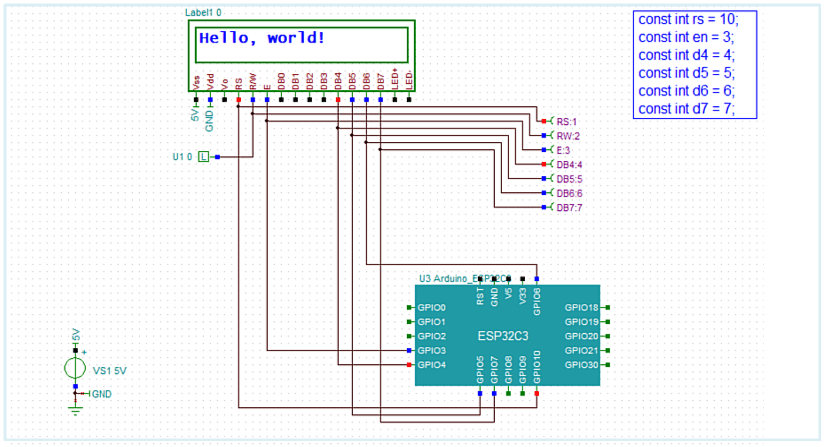
ESP32 Microcontroller Simulation
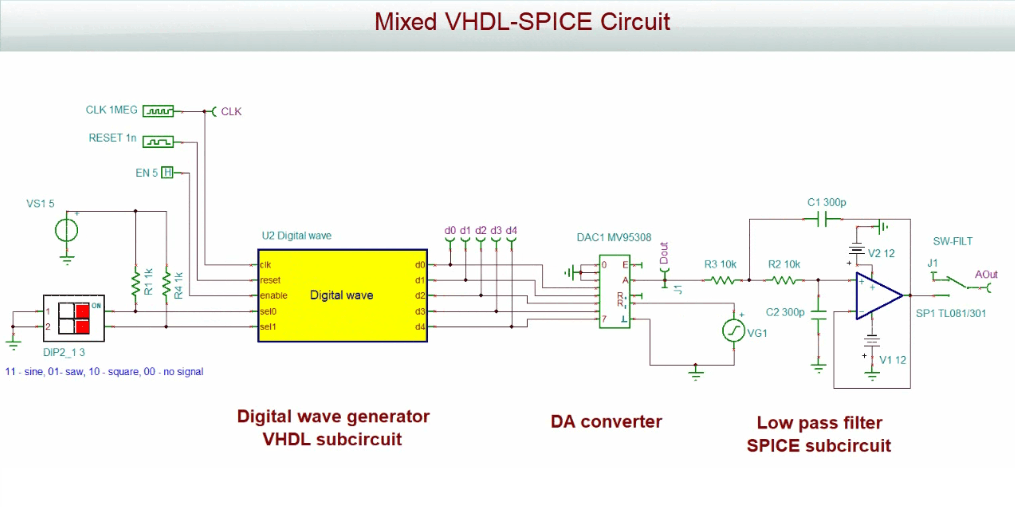
In addition to SPICE, TINA and TINACloud include 7 major Hardware Description Languages (VHDL, VHDL-AMS, Verilog, Verilog A&AMS, SystemVerilog, SystemC) for modeling modern, complex integrated circuits such as SAR and Sigma-Delta ADC, DAC converters with SPI, Digital power ICs with I2C and PM bus, and Digital filters.
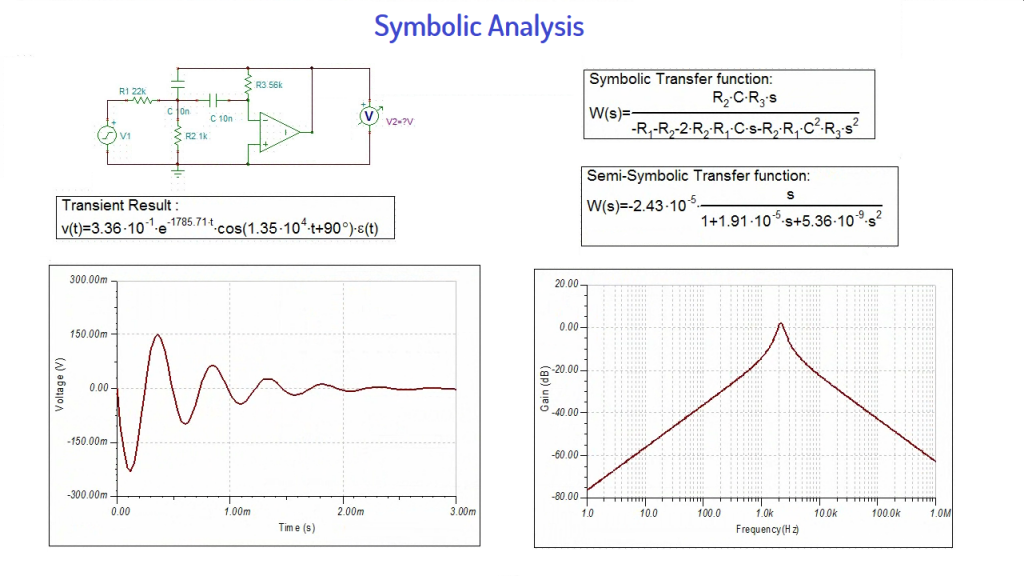
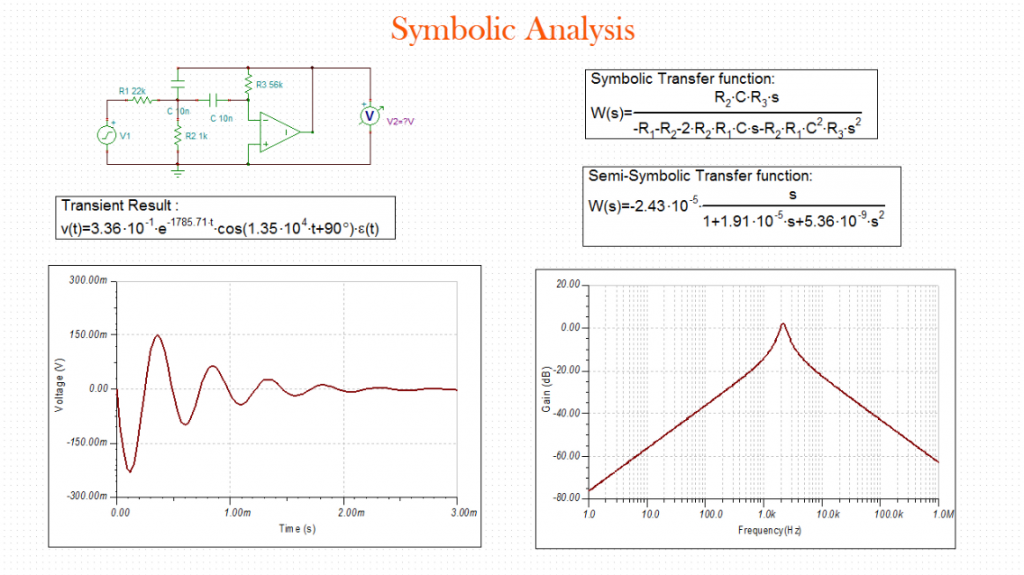
Unique Symbolic Analysis
Another unique feature of TINA is the Symbolic Analysis capability. This produces the closed-form expression of the transfer function, equivalent resistance, impedance, or response of analog linear networks.
- In DC and AC analysis mode, TINA derives formulas in full-symbolic or semi-symbolic form.
- In transient analysis, the response is determined as a function of time.
- Circuit variables can be referenced either as symbolic names or by value, and poles and zeros of linear circuits can be calculated and plotted.
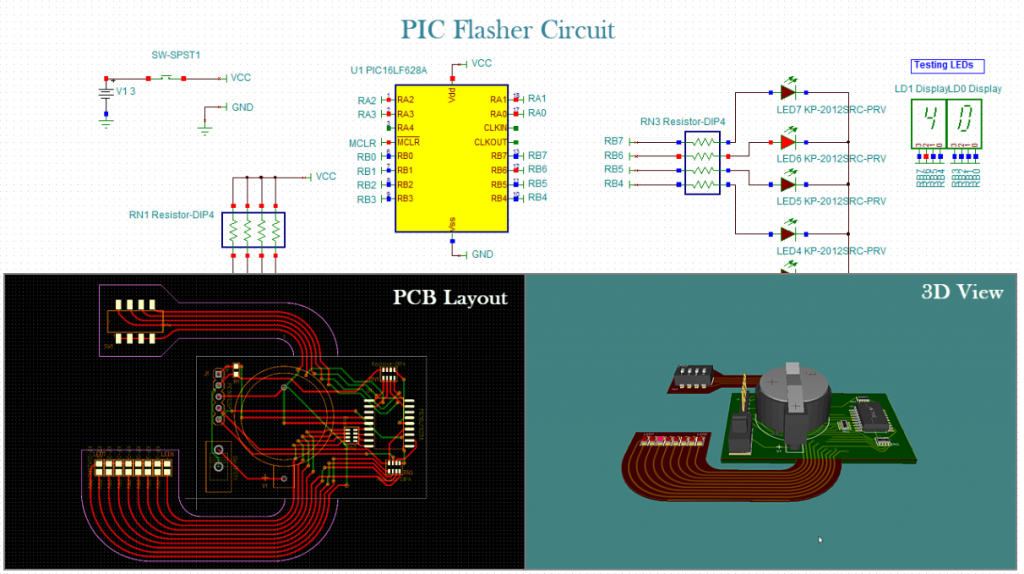
Microcontroller Support & Debugging
TINA supports more than 1,400 microcontrollers, including PIC, AVR, 8051, HCS, ARM, ESP32, ST, Arduino, XMC, and more. MCUs can be simulated in Mixed-Signal Analog-Digital circuits. The built-in debugger allows you to test your HEX, Assembly, or C code step-by-step, insert breakpoints, and view MCU registers, memory, or C statements and variable values.
Local & Remote Real-time Test & Measurement
TINA is far more than simulation software. You can use it with local or remote measurement hardware that allows real-time measurements controlled by TINA’s on-screen virtual instruments.
Integrated PCB Design
TINA Design Suite is extended with the fully integrated PCB Designer. Main features include:
- Autoplacement, autorouting, and “follow-me” trace placement.
- DRC, forward and backward annotation, and pin/gate swapping.
- Keep-in/out areas, thermal relief, fanout, and plane layers.
- Gerber and G-code output.
- Flexible PCB layout and 3D Enclosure support.
You can also import 3D Enclosures in industry-standard formats and visualize your PCB design with enclosures in 3D.
References
Texas Instruments
Since 2004, Texas Instruments, one of the largest semiconductor companies in the world, has been using TINA for its analog IC application support. Over this period, the usage of TINA has been extended with a large number of TI components and application circuits, and it is used regularly by a huge number of industrial customers. This great number of industrial projects also helped DesignSoft to expand and improve TINA as one of the fastest and most powerful circuit simulators.
Infineon Technologies
Since 2014, Infineon Technologies, one of the world leaders in the power electronics industry, has been using TINACloud as the engine for its online prototyping tool, Infineon Designer. TINACloud and TINA include thousands of models of Infineon’s LED drivers, high-voltage, high-power, RF, MCU and other parts, along with a large number of industrial prototypes and application circuits that can be processed and developed further in both TINA and TINACloud.
Conclusion
TINA and TINACloud are powerful design and analysis tools for the advancement of electronic circuits. New users will find the software robust and easy to learn, while experienced designers and educators will appreciate the rich component libraries and the integration of SPICE with HDL.
Whether you are a student, educator, or longtime circuit designer, TINA and TINACloud combine to deliver high-performance circuit analysis that is accessible both offline and online. Much more than another SPICE program, this is software that can help you advance your ideas, your product definition, and your understanding of complex electronic circuit behavior.
Watch our video about the new features of TINA v16 and TINACloud:

For more information, visit our websites:
Visit our YouTube channel: