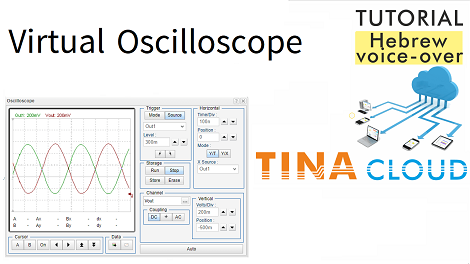
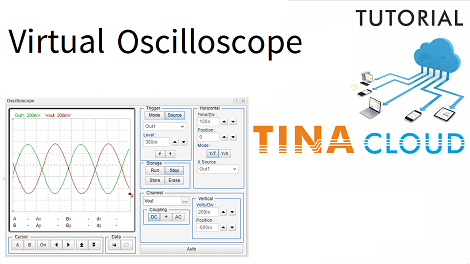
In this tutorial we will demonstrate how to use the virtual oscilloscope in TINACloud.
In practice we very often use an oscilloscope to measure, analyze and debug circuits in the time domain. So, it seems obvious that a simulated oscilloscope can be used in circuit simulation as well. However there are a few important things you must know about.
Even if you analyze the circuits in the computer with a simulated oscilloscope it is still simulation. You should not consider it as measurement, unless you use real time data acquisition for obtaining the data.
The simulated oscilloscope is very useful when you want to adjust some component values of small circuits and want to see the effect of the changes immediately, in order to fine-tune your circuit.
We present the use of the virtual oscillator through an example: Collpitts Oscillator circuit.
- First load the Colpitts.tsc circuit from the TINA Examples folder of TINACloud.
- Next invoke the Oscilloscope from the T&M menu,
- then press the Run button.
As a result , the Out1 signal appears. By default, the oscilloscope is in the “Auto” i. e., free running mode.
To get a steady state image you should enable triggering as follows:
- Set the Trigger Mode to Normal
- next, set Trigger Source to Out1
- finally, set the Trigger Level to 300m.
Consequently, the waveform is stabilized.
With the controls of the Oscilloscope you can make a lot of changes on the displayed waveform.
Here are a few:
By default, on the Oscilloscope rising edge triggering is used, so the display starts when the signal rises above the Trigger level.
- You can also set this to falling edge triggering where the display starts when the signal falls below the Trigger level.
- You can also bring in the Vout signal by selecting Vout under Channel
Let’s have the same vertical settings for Vout as for Out1.
- Finally, you can export the display into a diagram by pressing the Export to Diagram button under Data.
To watch our tutorial and learn more please click here.
You can learn more about TINA here: www.tina.com
You can learn more about TINACloud here: www.tinacloud.com